Superblock Area
Superblock Area in F2FS stores the core metadata information, including the capacity of storage devices, block size, available blocks and the index of other areas (SIT, NAT, SSA, Main) on the storage device.
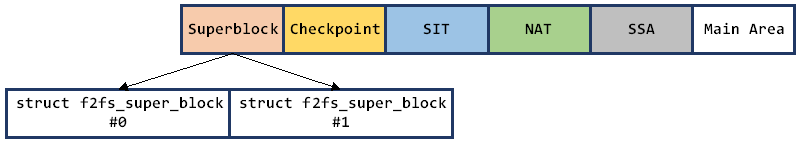
The Layout of Superblock on Storage Device
Superblock Area consists of two struct f2fs_super_block, which are backups of each other. When the file system is initialized, the two structures are first read from the front of the storage device, loading into memory, and the NAT, SIT, SSA Area are initialized according to the index information recorded by the struct f2fs_super_block.
struct f2fs_super_block is a physical structure stored on storage device. When it is loaded into memory, its information will be copied to an in-memory structure struct f2fs_sb_info. Their definitions are as follows:
Superblock Physical Structure
struct f2fs_super_block {
__le32 magic; /* Magic Number */
__le16 major_ver; /* Major Version */
__le16 minor_ver; /* Minor Version */
__le32 log_sectorsize; /* log2 sector size in bytes */
__le32 log_sectors_per_block; /* log2 # of sectors per block */
__le32 log_blocksize; /* log2 block size in bytes */
__le32 log_blocks_per_seg; /* log2 # of blocks per segment */
__le32 segs_per_sec; /* # of segments per section */
__le32 secs_per_zone; /* # of sections per zone */
__le32 checksum_offset; /* checksum offset inside super block */
__le64 block_count; /* total # of user blocks */
__le32 section_count; /* total # of sections */
__le32 segment_count; /* total # of segments */
__le32 segment_count_ckpt; /* # of segments for checkpoint */
__le32 segment_count_sit; /* # of segments for SIT */
__le32 segment_count_nat; /* # of segments for NAT */
__le32 segment_count_ssa; /* # of segments for SSA */
__le32 segment_count_main; /* # of segments for main area */
__le32 segment0_blkaddr; /* start block address of segment 0 */
__le32 cp_blkaddr; /* start block address of checkpoint */
__le32 sit_blkaddr; /* start block address of SIT */
__le32 nat_blkaddr; /* start block address of NAT */
__le32 ssa_blkaddr; /* start block address of SSA */
__le32 main_blkaddr; /* start block address of main area */
__le32 root_ino; /* root inode number */
__le32 node_ino; /* node inode number */
__le32 meta_ino; /* meta inode number */
__u8 uuid[16]; /* 128-bit uuid for volume */
__le16 volume_name[MAX_VOLUME_NAME]; /* volume name */
__le32 extension_count; /* # of extensions below */
__u8 extension_list[F2FS_MAX_EXTENSION][F2FS_EXTENSION_LEN];/* extension array */
__le32 cp_payload;
__u8 version[VERSION_LEN]; /* the kernel version */
__u8 init_version[VERSION_LEN]; /* the initial kernel version */
__le32 feature; /* defined features */
__u8 encryption_level; /* versioning level for encryption */
__u8 encrypt_pw_salt[16]; /* Salt used for string2key algorithm */
struct f2fs_device devs[MAX_DEVICES]; /* device list */
__le32 qf_ino[F2FS_MAX_QUOTAS]; /* quota inode numbers */
__u8 hot_ext_count; /* # of hot file extension */
__u8 reserved[314]; /* valid reserved region */
} __packed;
For a 50MB storage device, the information of a formatted f2fs_super_block is:
magic = -218816496
major_ver = 1
minor_ver = 10
log_sectorsize = 9
log_sectors_per_block = 3
log_blocksize = 12
log_blocks_per_seg = 9
segs_per_sec = 1
secs_per_zone = 1
checksum_offset = 0
block_count = 12800 # 50MB / 4KB = 12800
section_count = 17
segment_count = 24
segment_count_ckpt = 2 # checkpoint uses two segments (2MB * 2)
segment_count_sit = 2 # SIT: 2 segments
segment_count_nat = 2 # NAT: 2 segments
segment_count_ssa = 1 # SSA: 1 segments
segment_count_main = 17 # main area occupies 17 segments (17 * 2 = 34MB)
segment0_blkaddr = 512
cp_blkaddr = 512 # the start offset of Checkpoint Area on storage device
sit_blkaddr = 1536 # the start offset of SIT Area on storage device
nat_blkaddr = 2560 # the start offset of NAT Area on storage device
ssa_blkaddr = 3584 # the start offset of SSA Area on storage device
main_blkaddr = 4096 # the start offset of Main Area on storage device
root_ino = 3
node_ino = 1
meta_ino = 2
extension_count = 27
cp_payload = 0
feature = 0
encryption_level =
Superblock In-Mmemory Structure
As mentioned above,f2fs_sb_info is the memory form of f2fs_super_block. f2fs_sb_info records not only the information of f2fs_super_block, but also locks, GC thread, system mode, and the memory structure of NAT, SIT, etc.
struct f2fs_sb_info {
struct super_block *sb; /* pointer to VFS super block */
struct f2fs_super_block *raw_super; /* raw super block pointer */
struct rw_semaphore sb_lock; /* lock for raw super block */
/* for node-related operations */
struct f2fs_nm_info *nm_info; /* node manager */
struct inode *node_inode; /* cache node blocks */
/* for segment-related operations */
struct f2fs_sm_info *sm_info; /* segment manager */
/* for checkpoint */
struct f2fs_checkpoint *ckpt; /* raw checkpoint pointer */
/* for orphan inode, use 0'th array */
unsigned int max_orphans; /* max orphan inodes */
struct f2fs_mount_info mount_opt; /* mount options */
/* for cleaning operations */
struct mutex gc_mutex; /* mutex for GC */
struct f2fs_gc_kthread *gc_thread; /* GC thread */
unsigned int cur_victim_sec; /* current victim section num */
unsigned int gc_mode; /* current GC state */
};
f2fs_sb_info is initilized in init_sb_info function. We can find the variable struct f2fs_super_block *raw_super and this variable introduces the information on storage devices. struct f2fs_sb_info *sbi is a in-memory structure which copies data from raw_super.
static void init_sb_info(struct f2fs_sb_info *sbi)
{
// raw_supaer records the information from the storage device, as introduced in f2fs_super_block structure
struct f2fs_super_block *raw_super = sbi->raw_super;
int i, j;
sbi->log_sectors_per_block =
le32_to_cpu(raw_super->log_sectors_per_block);
sbi->log_blocksize = le32_to_cpu(raw_super->log_blocksize);
sbi->blocksize = 1 << sbi->log_blocksize;
sbi->log_blocks_per_seg = le32_to_cpu(raw_super->log_blocks_per_seg);
sbi->blocks_per_seg = 1 << sbi->log_blocks_per_seg;
sbi->segs_per_sec = le32_to_cpu(raw_super->segs_per_sec);
sbi->secs_per_zone = le32_to_cpu(raw_super->secs_per_zone);
sbi->total_sections = le32_to_cpu(raw_super->section_count);
sbi->total_node_count =
(le32_to_cpu(raw_super->segment_count_nat) / 2)
* sbi->blocks_per_seg * NAT_ENTRY_PER_BLOCK;
sbi->root_ino_num = le32_to_cpu(raw_super->root_ino);
sbi->node_ino_num = le32_to_cpu(raw_super->node_ino);
sbi->meta_ino_num = le32_to_cpu(raw_super->meta_ino);
sbi->cur_victim_sec = NULL_SECNO;
sbi->max_victim_search = DEF_MAX_VICTIM_SEARCH;
sbi->dir_level = DEF_DIR_LEVEL;
sbi->interval_time[CP_TIME] = DEF_CP_INTERVAL;
sbi->interval_time[REQ_TIME] = DEF_IDLE_INTERVAL;
clear_sbi_flag(sbi, SBI_NEED_FSCK);
for (i = 0; i < NR_COUNT_TYPE; i++)
atomic_set(&sbi->nr_pages[i], 0);
for (i = 0; i < META; i++)
atomic_set(&sbi->wb_sync_req[i], 0);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&sbi->s_list);
mutex_init(&sbi->umount_mutex);
for (i = 0; i < NR_PAGE_TYPE - 1; i++)
for (j = HOT; j < NR_TEMP_TYPE; j++)
mutex_init(&sbi->wio_mutex[i][j]);
init_rwsem(&sbi->io_order_lock);
spin_lock_init(&sbi->cp_lock);
sbi->dirty_device = 0;
spin_lock_init(&sbi->dev_lock);
init_rwsem(&sbi->sb_lock);
}